Molar Mass Chlorine
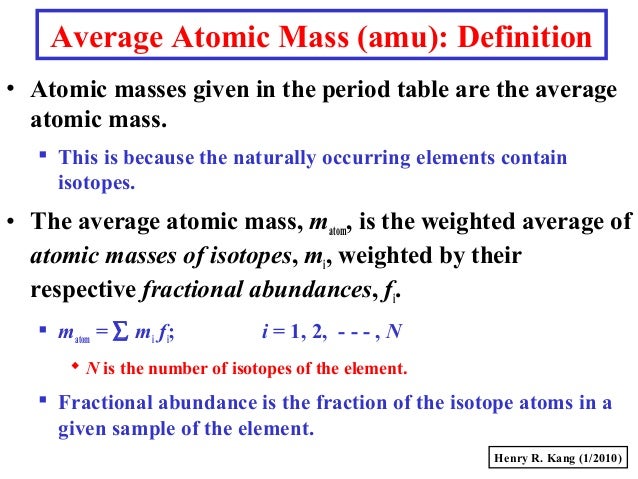
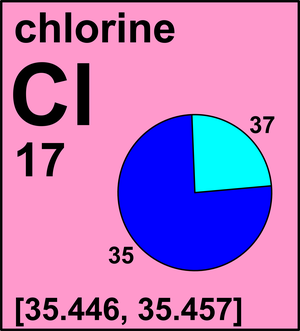
Use this periodic table for calculating molar mass for any chemical formula. Options for hiding the symbol or name of the elements provide a handy learning aid for memorizing the periodic table. IOS app is also available. My Work: SInce mass = number of mols x Molar mass, I first look for the molar mass of Ag2CO3, which is 275.75 g/mol. Chemistry 3.13 g of sodium (Na) react with 7.17 g of chlorine (Cl2) to produce 10.3 g of sodium chloride (NaCl). The molar mass is 35.5 g (according to the periodic table) The molar mass is generally the mass of one mole of that substance (chlorine). One mole of chlorine equals to 6.02214×10^23 atoms of chlorine. Be careful not to confuse molar mass with molecular mass, though. Molecular mass of chlorine would be mass of ONE chlorine atom. The average molar mass of chlorine is 35.5 g mol –1. The ratio of 35 Cl to 37 Cl in naturally occurring chlorine is close to: (1) 4: 1 (2) 1: 1 (3) 2: 1 (4) 3: 1. ›› Chlorine Pentafluoride molecular weight. Molar mass of ClF5 = 130.445016 g/mol. Convert grams Chlorine Pentafluoride to moles or moles Chlorine Pentafluoride to grams. Molecular weight calculation: 35.453 +.5 ›› Percent composition by element.
Ag+(aq) + Cl-(aq) → AgCl(s)
(i) moles of AgCl(s) precipitated
moles = mass ÷ molar mass
(ii) moles of chloride ion, Cl-, present
mole ratio AgCl:Cl- is 1:1
(iii) mass of chloride ion, Cl-, present in the seawater.
mass = moles × molar mass
 (that is, a percentage, w/v%)
(that is, a percentage, w/v%) (ii) grams of chloride per litre of seawater: g L-1
The concentration of chloride ions in seawater can also be given as a concentration in moles per litre:
Molar Mass Chlorine Atom
moles of chloride in 1 L of seawater: mol L-1 (molarity)
Ag+(aq) + Cl-(aq) → AgCl(s)
(i) moles of AgCl(s) precipitated
moles = mass ÷ molar mass
Cl Mw
(ii) moles of chloride ion, Cl-, present
mole ratio AgCl:Cl- is 1:1
(iii) mass of chloride ion, Cl-, present in the seawater.
mass = moles × molar mass
 (i) grams of chloride in 100 mL of seawater: g/100 mL
(i) grams of chloride in 100 mL of seawater: g/100 mL (that is, a percentage, w/v%)
(ii) grams of chloride per litre of seawater: g L-1
The concentration of chloride ions in seawater can also be given as a concentration in moles per litre:
moles of chloride in 1 L of seawater: mol L-1 (molarity)
