Install Windows On Virtualbox On Mac
Here I explain how to install Windows on a Mac using the (free) virtualization software, VirtualBox.
Install macOS Catalina on VirtualBox on Windows PC will essentially work straightforward similar to a Mac, and devotes most of your Windows power and its graphics card to running Catalina. How much ever you allocate, it will get more thirsty of power. The following article will show you how to install Mac OS X El Capitan on VMware on Windows PC. Thus, Apple and Mac want to produce new versions of their Mac OS operating system, and Mac OS X El Capitan is one of the old variant of the Mac OS operating system for both Mac. Step One: Install VirtualBox on Windows. Before you do anything, the first and foremost thing you’ll need to install VirtualBox. If you do have installed, you’ll need to update it to the latest version, that’s easy. You can do it from the VirtualBox itself without worry, just check for updates from File in the menu and if available.
VirtualBox is free software that allows you to install different operating systems on your machine. By using VirtualBox, you can install Windows on your Mac. This enables you to run Windows-only applications on your Mac.
Here are the main steps involved in installing Windows on a Mac:
- Download and Install VirtualBox
- Create a Virtual Machine
- Download and Install Windows
Here they are in more detail.
Download and Install VirtualBox
To run Windows on a Mac, you need to use virtualization software such as VirtualBox. While there are other options available (such as Parallels and VMware Fusion), VirtualBox is free. And while Bootcamp is also a free option, it doesn't let you run macOS and Windows simultaneously (you have to reboot the machine every time you want to switch to the other operating system). So with VirtualBox you get the best of both worlds — it's free, and it allows you to run both Windows and macOS simultaneously so you can switch between them as required without having to reboot.
Download VirtualBox
Go to the VirtualBox download page and click OS X Hosts.
Install VirtualBox
Double-click the VirtualBox.pkg icon to install VirtualBox. This will enable you to run VirtualBox from your Applications folder.
Create a Virtual Machine
Now that you've installed VirtualBox, you can create a virtual machine. This virtual machine is where you'll install Windows.
Launch VirtualBox
Launch VirtualBox via the Applications folder (just as you'd launch any other application).
Start the Wizard
Click New to start the process of creating a new virtual machine.
Name and Operating System
Enter a name for the virtual machine (make it descriptive, such as
Windows 10 or similar).Also choose Microsoft Windows and select the 64 bit version (unless you have reason to choose the 32 bit version).
Click Continue.
Set the Memory Allocation
Use the slider to specify how much memory is allocated to the virtual machine. I selected 4 GB (4000 MB), which should be sufficient to run SQL Server inside Windows. If your Mac has a lot more RAM, then you might be able to allocate more to the virtual machine.
Click Continue.
Hard Disk
Leave it at the default setting and click Create.
Hard Disk File Type
Leave it at the default setting and click Continue.
Storage on Physical Hard Disk
Leave it at the default setting and click Continue.
File Location and Size
Leave it at the default setting and click Create.
Done!
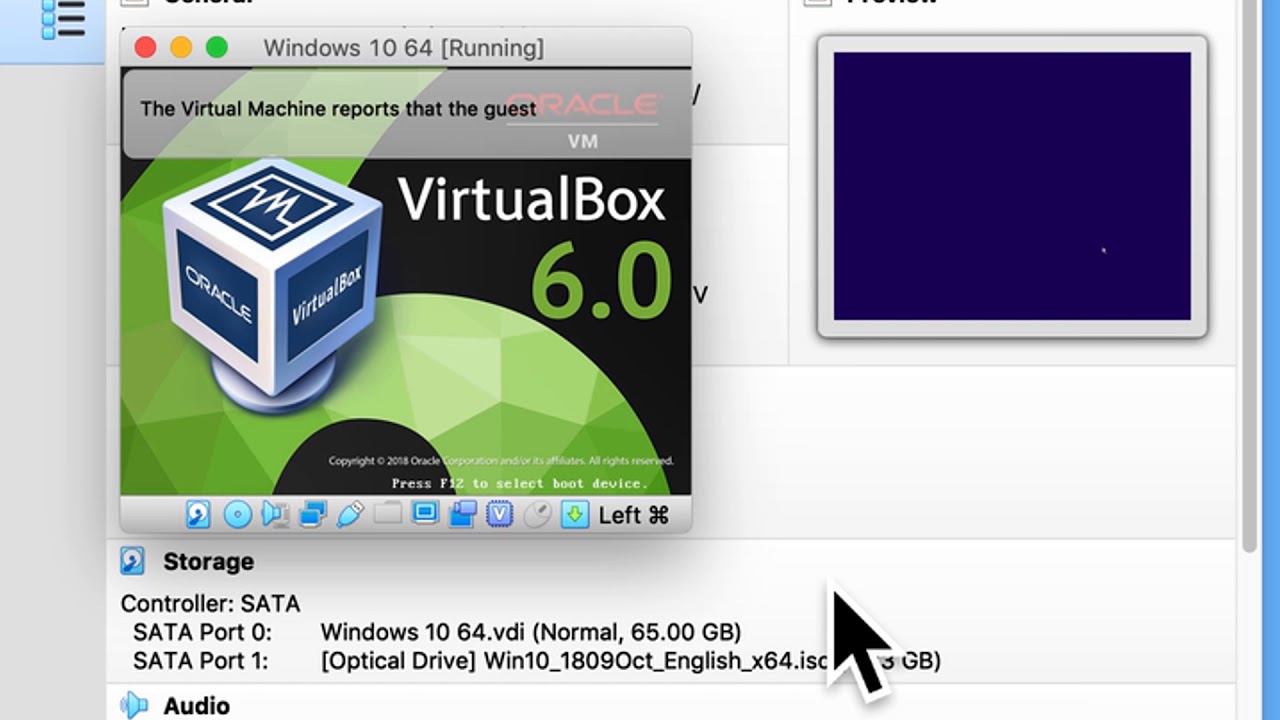
Your new virtual machine has been created. It appears in the left pane of the VirtualBox home screen.
This is where you launch your virtual machine from whenever you need to use Windows.
Download and Install Windows
Download the Windows Disk Image
Go to the Windows download page and select the latest version of Windows. Follow the prompts to download the ISO file to your Mac.
Alternatively, go to the Microsoft Evaluation Center and download a free evaluation trial. This is the option I used in this tutorial. This tutorial uses the Windows 10 Enterprise Evaluation edition (which is free to use for 90 days).
Download the file to your VirtualBox VMs folder (e.g. /Users/Dave/VirtualBox VMs/) or move it there once downloaded.
Start the Installation
Double-click on the virtual machine that you created previously.
Select the Windows Disk Image
Use the interface to browse to, and select, the Windows ISO file that you downloaded.
Click Start.
Select Language, etc
Select your language and other preferences, then click Next.
License Agreement
Select I accept the license terms and click Next.
Installation Type
Select Custom: Install Windows only (advanced).
Select the Drive
Here, the 50 GB drive (that you created when you created your virtual machine previously) should already be selected. If not, select it.
Click Next.
Select Keyboard Layout
Select your preferred keyboard layout and click Yes.
Add Another Keyboard?
Click Skip (unless you want to add another keyboard, in which case click Add layout and follow the prompts).
Join Domain
Microsoft wants you to sign in but for the purposes of this tutorial, we won't be doing that.
For this tutorial, click Domain join instead.
If you have an account with Office 365 or other business services, then feel free to sign in using that account instead.
Add Name
Add your name (or pseudonym) and click Next.
Confirm Password
Enter your password again to confirm and click Next.
Cortana?
Click either Yes or No depending on whether you want to use the Cortana personal assistant. (In this case I chose No.)
Privacy Settings
Disable any privacy settings you want to, then click Accept.
Finally.. Done!
Scp gui tool for mac. Windows is now installed. The Windows desktop is displayed, and you can now go ahead and start using Windows on your Mac!
If you're running macOS or Windows you have a few options for installing Docker. There's even a third way too, and we'll compare them here.
Quick Jump: OS and Hardware Requirements|Pros and Cons|Which One Should I Use?
If you’re on macOS or Windows you can install Docker with:
- Docker for Mac / Windows (now known as Docker Desktop)
- Docker Toolbox
- Running your own Virtual Machine and installing Docker yourself
All 3 of those options have their own pros and cons and in this article we’re going to cover them. If you’re looking for a high level overview of what Docker for Mac / Windows and Docker Toolbox is, then check out this article on getting to know Docker’s ecosystem.
OS and Hardware Requirements
It’s helpful to know what you can install before we compare everything, so let’s do that:
Docker for Mac (Docker Desktop)
Docker for Mac requires that you’re running Mojave 10.14+ or newer with an Intel CPU. M1 support is on its way.
You can run VirtualBox 6+ alongside Docker Desktop. Manual line break excel 2016 mac. This is pretty useful because you might have some legacy apps running in Vagrant / VirtualBox to deal with (I know I do!).
Docker for Windows (Docker Desktop)
As of May 27th 2020, Microsoft released Windows 10 build 2004 (Spring 2020) that allows you to run Docker Deskop on all editions of Windows 10, including Home thanks to WSL 2.
As of August 2020, Microsoft enabled WSL 2 support for Windows 10 builds 1903 + 1909.
Nba 2k2. For years prior to that you could only run it on Windows Pro, Enterprise or any edition that had Hyper-V available, but since August 2020 pretty much all supported versions of Windows 10 can use Docker Desktop.
You can also run VirtualBox 6+ alongside Docker Desktop too in case you have older projects using VirtualBox (perhaps with Vagrant too).
Docker Toolbox
Prior to mid-2020 this was still a reasonable way to run Docker on machines that couldn’t run Docker Desktop, but that’s no longer the case.
It’s now considered legacy and as of late 2020 it’s been officially deprecated.
Unless you’re using unsupported versions of Windows or have a really really ancient Mac you shouldn’t need to ever use this tool.
But if you’re in a pinch and you absolutely must use it, technically it’s still available at https://github.com/docker/toolbox/releases, but it’s no longer maintained by Docker.
Your own Virtual Machine
Docker will happily run inside of VirtualBox, VMWare Workstation or any other Type 1 / 2 Hypervisor that’s running a major distribution of Linux as a guest OS.
If for whatever reason you can’t use Docker Desktop then this solution would be better than using Docker Toolbox since you can install supported versions of Docker and you have full control over the environment.
Pros and Cons
Now for the good stuff!
Docker for Mac / Docker for Windows (Docker Desktop)
Pros
Offers the most “native” experience, you can easily use any terminal you you want since Docker is effectively running on
localhostfrom macOS / Windows’ POV.Docker is heavily developing and polishing this solution.
Cons
On certain macOS hardware combos the volume performance can be a little slow.
I can legit say there are not any “wow this sucks!” cons for Windows, it’s really solid.
Docker Toolbox
Pros
- Offers an “out of the box” Docker experience if you have no other choice.

Install Windows On Virtualbox From Usb On Mac
Cons
It’s deprecated by Docker and will receive no future maintenance.
You need to either use the Docker Quickstart Terminal, or configure your own terminal to connect to the Docker Daemon running a VM.
Not a native solution, so you’ll need to access your Docker Machine’s IP address if you’re developing web apps. Example:
192.168.99.100instead oflocalhost.Unless you jump through hoops, your code needs to live in your Windows user directory such as
C:UsersNicksrcmyapp. Otherwise Docker won’t be able to find it.Suffers from typical VirtualBox edge case bugs and mount performance issues.
Your own Virtual Machine
I’m not going to bother listing a pros and cons here because I wouldn’t recommend doing this UNLESS you’re stuck on Windows 7 / 8 or an older version of Windows 10 like 1809.
But more on that in a bit.
Which One Should I Use?
If you’re interested in Docker, you’re a smart person and you probably came to the conclusion that using Docker for Mac or Docker for Windows is a good idea as long as you can run it.
My recommendation would be to try Docker for Mac / Windows first, and test it against your actual use cases. The performance issues may or may not be a concern, especially since everyone’s needs and computer specs are different.
Install Windows On Macos Virtualbox
I’ve been using Docker Desktop on Windows for full time development since late 2018 and it’s been nothing short of fantastic. Currently I use it with WSL 2, but it was really good with WSL 1 along with Hyper-V too.
Stuck on an Old Version of Windows and Like Linux?
I want to mention a “roll your own VM” solution for Windows users because I feel like there’s an even better way to run Docker on Windows if you also like Linux and are stuck not being able to use modern versions of Windows 10.
It involves running VMWare Player in a special mode called “Unity mode”. This basically allows you to run Windows and Linux together seamlessly as 1 operating system.
There’s no dual booting and Linux applications (even graphical apps) run in their own floating windows. Then you can install Docker natively on Linux inside of the VM.
The performance is excellent and the entire set up is free too.
I used this set up for about 5 years until Docker Desktop was available. It gives you the best of both worlds. For example, I run high end audio / video apps on Windows while recording courses and screencasts that cover Linux content. It all works great (even for full time development).
Install Mac Os Virtualbox
You can watch a video guide and see screenshots on how to do that in this post on creating an awesome Linux development environment in Windows.
Install Virtualbox On Windows 10
Are you using the Docker Toolbox, Docker for Mac / Windows or your own VM?
